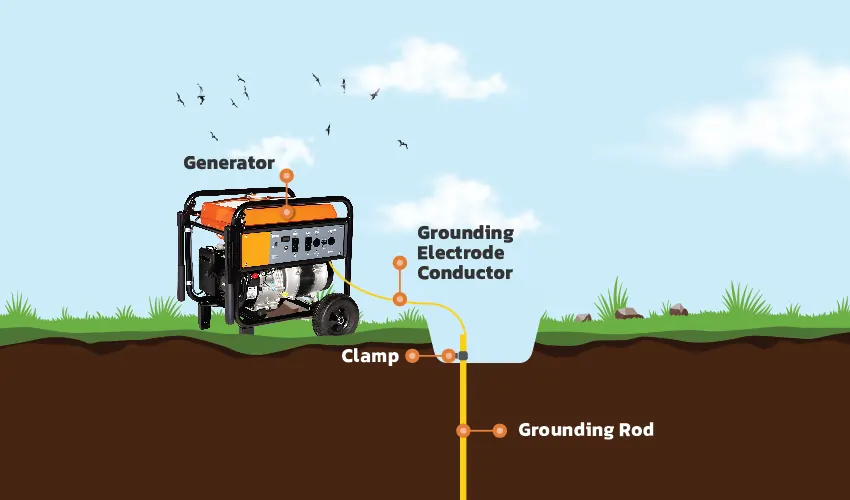
This essential practice involves establishing a secure connection between the generator and the ground to prevent electric shocks and protect both people and equipment.
Whether using a grounding rod or alternative methods, understanding and implementing proper grounding procedures are crucial for a safe and reliable camping or outdoor generator experience.
What Happens If You Don’t Ground a Generator?
Ground a inverter portable generator is an important safety measure that helps prevent electrical shock and protects both people and equipment. If you don’t ground a generator properly, several potential problems and risks can arise:
- Electric Shock Hazard: Grounding provides a path for electrical currents to flow safely to the ground. Without proper grounding, there is an increased risk of electric shock for anyone in contact with the generator or connected equipment.
- Equipment Damage: Lack of grounding can lead to electrical surges and improper functioning of connected electrical devices. This can result in damage to sensitive electronics, appliances, or the generator itself.
- Fire Hazard: Inadequate grounding can increase the risk of electrical fires. Sparks or overheating in the electrical system may ignite surrounding materials.
- Code Violations: Failure to ground a generator in accordance with local electrical codes and regulations can result in legal and regulatory issues. Building codes typically require proper grounding to ensure the safety of the electrical system.
- Interference with Electronics: Without proper grounding, there may be interference with sensitive electronic equipment due to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radiofrequency interference (RFI). This interference can affect the performance of electronic devices.
To avoid these risks, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and local electrical codes when installing and operating a generator. This often includes connecting the generator to a grounding electrode system, which may involve using grounding rods and conductors to create a proper grounding path.
How to Ground a Generator without a Grounding Rod?
Establish a ground for the generator is an essential safety practice to prevent electric shocks and ensure the proper functioning of electrical equipment. While using a grounding rod is a common method, there are alternative ways to ground a generator if a grounding rod is not available. Here are some options:
- Metal Water Pipe:
- Ensure the water pipe is metal and extends underground.
- Use a suitable grounding clamp to connect a copper or aluminum wire to the metal water pipe.
- Connect the other end of the wire to the generator’s grounding terminal.
- Metal Conduit:
- If your generator is located near a metal conduit that goes into the ground, you can use it as a grounding path.
- Connect a grounding wire to the metal conduit using a grounding clamp.
- Attach the other end of the wire to the generator’s grounding terminal.
- Metal Structure:
- If there is a metal structure, such as a building or a metal frame, near the generator, you can use it for grounding.
- Connect a grounding wire to the metal structure using a grounding clamp.
- Connect the other end of the wire to the generator’s grounding terminal.
- Grounding to a Grounded Outlet:
- If your generator has a grounded outlet, you may use that as a temporary solution.
- Connect a wire from the generator’s grounding terminal to the ground pin of the grounded outlet.
- Ensure that the outlet is connected to a properly grounded electrical system.
How to Ground a Generator When Camping?
When camping with a generator, it’s important to follow proper grounding procedures to ensure safety. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to ground a generator when camping:
- Check Local Regulations:
- Before grounding your generator, be aware of any specific regulations or requirements for generator use in the camping area. Some campgrounds may have rules regarding generator use and grounding.
- Use a Grounding Rod (if available):
- If you have access to a grounding rod, it’s the most effective way to ground a generator.
- Drive the grounding rod into the ground, ensuring it is deep enough to establish a good connection with the soil.
- Connect a copper or aluminum grounding wire from the generator’s grounding terminal to the grounding rod using a suitable grounding clamp.
- Alternative Grounding Methods:
- If a grounding rod is not available, consider alternative grounding methods such as using a metal water pipe, metal conduit, or a metal structure (as mentioned in the previous response).
- Ensure a secure connection between the generator’s grounding terminal and the chosen grounding point.
- Avoid Grounding to a Neutral Conductor:
- Never use the neutral conductor (white wire) as a substitute for grounding. It does not provide the same level of safety as a proper grounding system.
- Use a Grounding Mat (Optional):
- Some campers use grounding mats designed for generators. These mats provide a conductive surface that can be placed on the ground beneath the generator, creating a low-resistance path to the earth.
- Check for Proper Grounding:
- Once the generator is connected to the grounding point, check for continuity using a multimeter to ensure that a proper grounding connection is established.
- Secure Wiring:
- Make sure that all wiring is securely connected and insulated to prevent any hazards.
- Follow Generator Manual Instructions:
- Always refer to the generator’s manual for specific grounding instructions provided by the manufacturer. Different generators may have variations in their grounding requirements.
- Regularly Inspect and Maintain:
- Periodically inspect the grounding system to ensure its integrity. Loose connections or damage should be addressed promptly.
Conclusion
Grounding a inverter portable generator is a critical safety measure to prevent electric shocks and ensure proper equipment function. Using a grounding rod or alternative methods such as metal pipes or structures establishes a reliable path for electrical currents to dissipate safely into the ground. Always adhere to local regulations, the manufacturer’s instructions, and regularly inspect the grounding system to maintain its integrity. Proper grounding is essential for safe camping and outdoor generator use.