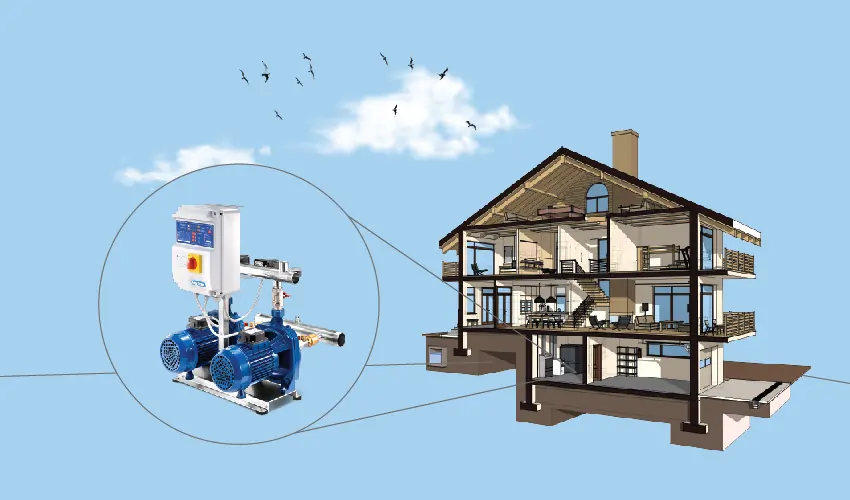
Booster Pump Installation
This brief guide provides key considerations for the installation process, emphasizing the importance of proper placement and compliance with regulations for optimal performance.
How to Install Water Booster Pump?
Installing a water booster pump involves a series of steps to ensure proper functioning and safety. Keep in mind that these instructions are general guidelines, and it’s crucial to follow the specific manufacturer’s instructions provided with your pump. Additionally, local plumbing codes and regulations may vary, so be sure to check and comply with them. Here’s a general guide for installing a water booster pump:
Materials and Tools
- Water booster pump
- Pressure tank (if not integrated into the pump)
- Piping and fittings
- Pipe wrench
- Teflon tape
- Adjustable wrench
- Screwdriver
- Pressure gauge
- Electrical wiring and tools (if the pump requires electrical connection)
Steps
Selecting the Location
- Choose a location for the pump that is dry, well-ventilated, and easily accessible for maintenance.
- The pump should be close to the water source and electrical supply.
Preparing the Pump
- Read the manufacturer’s instructions thoroughly.
- Make sure the pump is suitable for the type of water system you have.
- If the pump is not self-priming, ensure it is installed below the water level.
Preparing the Pipes
- Measure and cut the necessary pipes to connect the pump to the water supply and distribution system.
- Clean the pipe ends and remove any burrs.
Fittings and Connections
- Install the appropriate fittings (check valves, pressure relief valves, etc.) as specified by the manufacturer.
- Use Teflon tape on threaded connections to ensure a tight seal.
Connecting to the Water Supply
- Connect the intake side of the pump to the main water supply.
- Install a check valve to prevent water from flowing back into the supply.
Connecting to the Distribution System
- Connect the discharge side of the pump to the distribution system.
- Install a pressure tank if not integrated into the pump. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for tank installation and pre-charge pressure.
Pressure Gauge
- Install a pressure gauge on the system to monitor pressure.
- Place it on the discharge side of the pump.
Electrical Connection
- If the pump requires an electrical connection, follow the wiring instructions provided by the manufacturer.
- Ensure that the electrical work is done by a qualified professional if needed.
Testing
- Open the water supply and check for any leaks.
- Turn on the pump and check the pressure.
- Adjust the pressure settings if necessary.
Regular Maintenance
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance, which may include periodic inspections, lubrication, and cleaning.
How to Install Water Booster Pump for Home?
Installing a water booster pump for your home can be a relatively straightforward process, but it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions specific to your pump model. In general the steps of setting up a booster pump system in home is like the steps that we discuss in previous section.
Where to Install Booster Pump?
The installation location of a booster pump depends on the specific needs of your water system and the type of booster pump you have. Here are some general guidelines to help you decide where to install a booster pump:
Near the Water Source
- Install the booster pump as close to the water source as possible. This is usually where the main water supply enters your property.
Before Pressure Tank (if applicable)
- If you have a pressure tank as part of your system, install the booster pump before the pressure tank. The pump pressurizes the water, and the tank helps maintain a steady pressure in the distribution system.
Dry and Ventilated Location
- Choose a location that is dry, well-ventilated, and easily accessible for maintenance. Avoid areas prone to flooding or excessive moisture.
Accessibility
- Ensure easy access to the booster pump for regular maintenance and troubleshooting. This includes having enough space around the pump and providing clear access to any controls or adjustment settings.
Below Water Level (for Non-Self-Priming Pumps)
- If your booster pump is not self-priming, install it below the water level to ensure that it is always primed with water.
Secure Mounting
- Securely mount the pump on a stable surface to minimize vibrations and reduce noise. Some pumps may have specific mounting requirements outlined in the manufacturer’s instructions.
Electrical Connections
- If the booster pump requires an electrical connection, ensure that there is a nearby power source. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper wiring and consider consulting an electrician if needed.
Check Valve
- Install a check valve on the suction side of the booster pump to prevent backflow and maintain prime.
Pressure Gauge
- Install a pressure gauge on the discharge side of the pump to monitor the pressure in the system.
Compliance with Codes
- Ensure that your installation complies with local plumbing codes and regulations. This may include considerations for electrical work, plumbing connections, and other safety requirements.
When to Install a Booster Pump?
Booster pump mounting is recommended in various situations where there is insufficient water pressure to meet the demands of your plumbing fixtures and appliances. Here are some common scenarios when installing a booster pump may be necessary or beneficial:
Low Water Pressure
- If you experience consistently low water pressure throughout your home, a booster pump can help increase the pressure, ensuring a more reliable and satisfying flow.
Multi-Story Homes
- In multi-story homes, water pressure tends to decrease as you move higher in the building. A booster pump can help maintain adequate pressure on upper floors.
Large Homes with Extensive Plumbing
- Larger homes with numerous bathrooms, kitchens, and appliances may experience a drop in water pressure. A booster pump can enhance pressure to accommodate the increased demand.
Homes in Elevated Areas
- If your home is situated in an elevated area, where water pressure from the municipal supply is naturally lower, a booster pump can help compensate for the elevation difference.
Use of Rainwater or Well Water
- Homes relying on rainwater harvesting systems or well water may benefit from a booster pump to ensure sufficient pressure for all water outlets.
Improving Irrigation Systems
- Booster pumps are commonly used in irrigation systems to provide adequate water pressure for efficient watering of lawns and gardens.
Upgrading Plumbing Systems
- When upgrading or remodeling your home and adding new plumbing fixtures, a booster pump may be necessary to maintain satisfactory water pressure.
Commercial Buildings
- Commercial establishments, such as restaurants or offices, with high water demand may require booster pumps to ensure consistent and reliable water pressure for various activities.
Appliances Requiring Higher Pressure
- Some appliances, such as certain types of showers or water heaters, may work more efficiently with higher water pressure. A booster pump can enhance performance.
Watering Systems for Fire Protection
- Homes with fire protection systems, such as sprinklers, may benefit from booster pumps to ensure an adequate water supply and pressure during emergencies.
Conclusion
Proper Booster pump setup, considering factors like location, accessibility, and compliance with regulations, ensures optimal performance and reliability.