Best Water Pump
At its core, the function of a water pump is to facilitate the movement of water through suction or pressure mechanisms. This simple yet vital process is essential for everyday activities such as supplying water to homes, irrigating fields, and assisting in various industrial operations. The evolution of water pumps over the years has led to the development of various types that cater to specific needs and applications, each varying in size, power source, and capacity, so it is crucial to choose best water pump. While the fundamental purpose of a water pump remains consistent – to transport water – the diversity of designs and functionalities available today make them indispensable tools in modern society, underscoring their importance across multiple sectors.
What Is the Importance of Water Pump?
The importance of water pumps in modern society cannot be overstated. These devices are fundamental in ensuring the efficient movement and management of water, a critical resource for human survival, industrial operations, and environmental sustainability.
In residential settings, water pumps are key to supplying homes with clean water and sewage systems, making modern living more hygienic and convenient. In agriculture, they are indispensable for irrigation, helping to sustain crop production and thereby playing a crucial role in food security. Industrial applications are equally varied, with water pumps being used in everything from cooling systems to waste management, highlighting their versatility and importance in maintaining industrial processes. Moreover, in regions prone to flooding, water pumps are vital for flood control, mitigating potential damage to property and loss of life. The role of water pumps in conserving and managing water resources also cannot be ignored, especially in the context of increasing environmental concerns and the need for sustainable water management practices.
What Are the Best Water Pumps for Specific Home Applications?
When selecting the best water pump for specific home applications, it’s essential to consider the unique requirements of each task. Here’s a look at some common home applications and the types of water pumps that are generally well-suited for each.
Domestic Water Supply
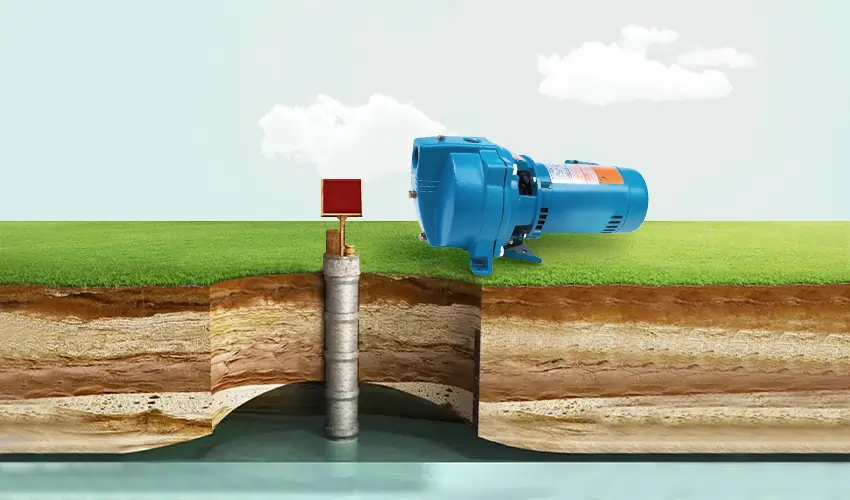
For the general supply of water to a home, especially in areas where water pressure is low, a centrifugal pump or a submersible pump is often ideal. These pumps can efficiently transport water from a source, like a well or a storage tank, to the home.
Garden Irrigation
For watering gardens, an irrigation pump, typically a centrifugal pump, is suitable. These pumps can provide the right amount of water pressure for sprinkler systems or for direct hose feeding.
Swimming Pools
Pool pumps, which are a type of centrifugal pump, are used to circulate water in swimming pools, keeping the water clean and sanitary. They are designed to handle a large volume of water and to operate for extended periods.
Sump Pumps
In homes with basements, especially in areas prone to flooding, a sump pump is essential. This pump type, usually a submersible pump, is designed to remove water that accumulates in a sump basin, preventing water damage and protecting the structural integrity of the home.
Booster Pumps
In homes experiencing inconsistent water pressure, a booster pump can be installed. These pumps increase the water pressure and flow rate, ensuring an adequate supply of water for showers, taps, and appliances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Water Pump
Choosing the right water pump for a specific application requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a water pump:
- Flow Rate: This refers to the volume of water that a pump can move within a given time period, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM). Understanding the required flow rate for your application is crucial for selecting a pump that can handle the demand.
- Head Pressure: Head pressure, or simply ‘head,’ measures the height to which a pump can raise water. It’s important to calculate the total head requirement, including both the vertical lift and the friction loss in the piping, to ensure the pump can effectively deliver water to the desired height.
- Power Source: Consider the available power sources for running the pump. Options typically include electric, gasoline, diesel, or solar-powered pumps. The choice will depend on the pump’s location, availability of power sources, and operational costs.
- Pump Type: Different types of pumps (e.g., centrifugal, submersible, and booster) are suited for different applications. Understanding the nature of the application, whether it’s for irrigation, sewage movement, water supply, etc., is crucial in selecting the appropriate pump type.
- Energy Efficiency: An energy-efficient pump will save costs in the long run, making it an important consideration, especially for pumps that will run frequently or continuously.
- Installation and Maintenance: Consider the ease of installation and the maintenance requirements of the pump. Some pumps may require professional installation and regular maintenance, which can add to the overall cost.
- Size and Space Constraints: The physical size of the pump and the space available for installation can influence your choice. Ensure that the pump fits comfortably within the designated area and that there’s enough space for maintenance activities.
- Cost: While the initial cost is an important consideration, also factor in the operating and maintenance costs over the pump’s lifespan to understand the total cost of ownership.
- Noise Level: Especially for residential applications, the noise level of the pump can be a significant factor. Quieter pumps may be preferable in settings where noise could be a disturbance.
What Are the Professional Water Pump Applications?
Top water pumps applications span a wide range of industries and sectors, each with specific requirements and challenges. These applications often demand high durability, efficiency, and capacity from the pumps used. Here’s an overview of some of the key professional water pump applications:
- Agriculture and Irrigation
- In agriculture, pumps are used for irrigation, providing water to crops in large fields. They must be capable of delivering varying water volumes and withstand outdoor conditions.
- Construction Sites
- Water pumps in construction are used for dewatering, removing excess water from excavation sites, foundations, or trenches. These pumps need to handle muddy water and debris, and be robust enough for harsh construction environments.
- Mining Operations
- In mining, pumps are used for dewatering mine shafts, managing water in processing operations, and controlling slurry. These applications often require heavy-duty pumps that can handle abrasive and corrosive fluids.
- Municipal Water and Wastewater Management
- This includes water treatment plants and sewage treatment facilities. Pumps in these settings move large volumes of water and wastewater and must meet stringent regulatory standards for sanitation and environmental protection.
- Chemical and Process Industries
- Pumps in these industries are used for transferring various chemicals, acids, and other hazardous materials. They must be made of materials that can resist corrosion and chemical attack.
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Pumps in this sector are used for a variety of tasks, including oil transfer, gas processing, and managing byproducts. They often require high-pressure capabilities and explosion-proof designs.
- Firefighting and Emergency Services
- High-pressure water pumps are used in firefighting to deliver water at great force. These pumps must be highly reliable, portable, and capable of functioning under extreme conditions.
- Flood Control and Drainage
- Large, high-capacity pumps are used in flood control to move large volumes of water during heavy rains or natural disasters to prevent or mitigate flooding.
- Power Generation
- In power plants, pumps are used for boiler feed water, cooling systems, and condensate extraction. These pumps are critical components and are designed for high efficiency and reliability.
Conclusions
In conclusion, water pumps play an indispensable role in a myriad of applications, ranging from residential uses to complex industrial processes. Their significance lies not only in their ability to efficiently move and manage one of our most vital resources – water – but also in their versatility and adaptability to various environments and requirements. From irrigating vast agricultural lands to ensuring the smooth operation of industrial plants, water pumps are at the heart of many critical operations.
This article has highlighted the diverse contexts in which water pumps are used, each demanding specific features and capabilities. We’ve seen how crucial it is to choose the right top-rated water pumps, considering factors like flow rate, head pressure, material compatibility, and energy efficiency. Advancements in pump technology continue to evolve, driven by the need for more efficient, reliable, and environmentally friendly solutions.