A diesel generator set is known for its reliability and versatility, it converts diesel fuel into electrical energy, making it a valuable source of power in diverse applications, from backup in emergencies to continuous prime power.
What is the Definition of Diesel Generator Sets and Their Role in Power Generation?
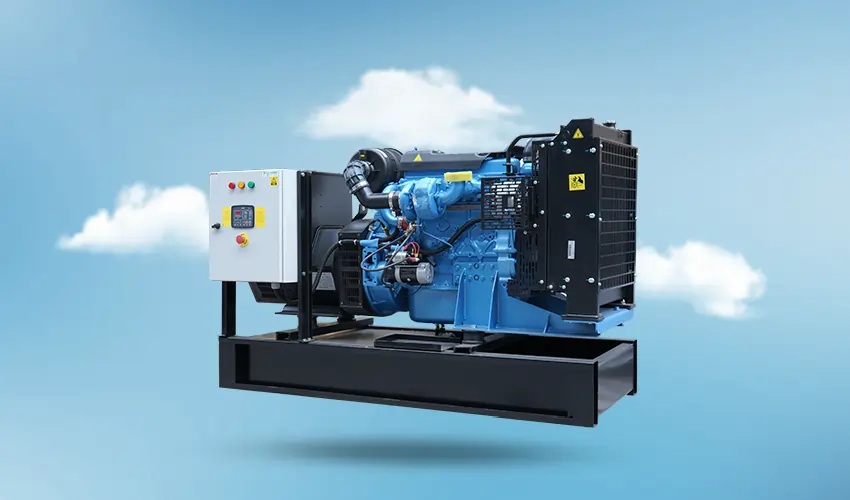
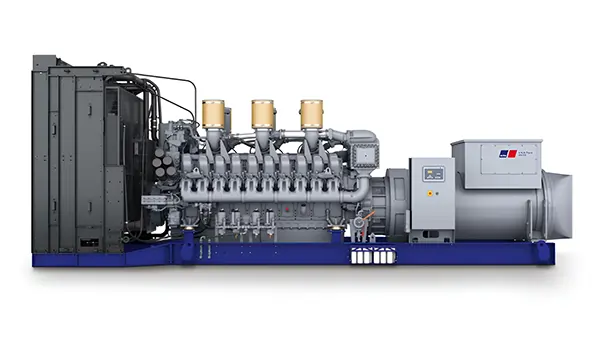
A diesel generator set, often referred to simply as a diesel generator or genset, is a combination of a diesel engine and an electric generator (alternator) used to generate electrical energy. These generator sets are commonly employed for providing standby or backup power, as well as prime power in areas where a stable electrical supply from the grid is unavailable or unreliable. Here’s a breakdown of the components and their roles in a diesel generator set:
Diesel Engine: The diesel engine is the primary component responsible for converting chemical energy in diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. Diesel engines are known for their durability, fuel efficiency, and reliability. They are well-suited for continuous operation over extended periods.
Electric Generator (Alternator): The electric generator, or alternator, is connected to the diesel engine and converts the mechanical energy produced by the engine into electrical energy. Alternators in diesel generator sets typically produce alternating current (AC), which can then be used to power electrical loads directly or converted to direct current (DC) if needed.
Control Panel: The control panel houses the necessary controls and instrumentation for monitoring and regulating the generator set’s operation. It includes features such as start/stop controls, voltage and frequency regulation, safety shutdowns, and other monitoring devices. Fuel System: Diesel generator sets have a fuel system that stores and supplies diesel fuel to the engine for combustion. The fuel system also includes filters to ensure the quality and cleanliness of the fuel, preventing damage to the engine.
Cooling System: Diesel engines generate a significant amount of heat during operation. The cooling system is responsible for maintaining optimal operating temperatures to prevent overheating. Common cooling methods include air cooling or liquid cooling using a radiator.
Roles in Power Generation
Standby Power: Diesel generators are often used as backup power sources in critical facilities such as hospitals, data centers, and emergency services. They automatically start and provide power in the event of a grid outage, ensuring continuity of essential operations.
Prime Power: In areas where a reliable grid connection is unavailable, diesel generator sets can serve as the primary source of power (prime power) for extended periods. Remote Power Generation: Diesel generators are commonly employed in remote locations or construction sites where grid power is not accessible.
Peak Shaving: Diesel generators can be used to supplement grid power during peak demand periods, helping to manage high electricity demand.
What are the Key Components of a Diesel Generator Set?
A diesel generator set comprises several key components, each playing a crucial role in the generation and delivery of electrical power. Here are the main components of a typical diesel generator set:
Diesel Engine: The diesel engine is the primary component that converts chemical energy from diesel fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. It serves as the main power source for the generator set.
Electric Generator (Alternator): The electric generator, also known as an alternator, is connected to the diesel engine and converts the mechanical energy produced by the engine into electrical energy. It generates alternating current (AC) electricity.
Fuel System: The fuel system stores and supplies diesel fuel to the engine for combustion. It typically includes a fuel tank, fuel pump, filters, and fuel injectors.
Cooling System: Diesel engines generate heat during operation, and a cooling system is employed to maintain optimal operating temperatures. This system may use air cooling or liquid cooling with a radiator.
Exhaust System: The exhaust system is responsible for directing the combustion gases away from the engine. It includes components such as the exhaust manifold, muffler, and exhaust pipe.
Lubrication System: The lubrication system ensures that moving parts within the engine are properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear. It typically includes an oil pump, oil filter, and an oil sump.
Battery and Starting System: A battery is used to provide electrical power for starting the diesel engine. The starting system includes a starter motor that cranks the engine to initiate the combustion process. Control Panel: The control panel houses the necessary controls and instrumentation for monitoring and regulating the generator set. It includes features such as start/stop controls, voltage and frequency regulation, and safety shutdowns.
Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator controls the output voltage of the generator to maintain a stable and consistent electrical output. Governor: The governor regulates the speed of the diesel engine, ensuring that it operates at a constant speed under varying load conditions. This helps maintain a stable frequency in the generated power.
Air Intake System: The air intake system provides clean air to the diesel engine for the combustion process. It includes components like an air filter to remove contaminants from the incoming air.
Control and Monitoring Sensors: Various sensors, such as temperature sensors, pressure sensors, and fuel level sensors, are integrated into the system to monitor critical parameters and provide feedback to the control panel.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Diesel Generator Set?
Diesel generator sets offer several advantages and disadvantages, and their suitability depends on the specific requirements of the application. Here are some key advantages and disadvantages of using diesel generator sets:
Advantages
Reliability and Durability: Diesel generator sets are known for their robustness and reliability. They are durable and can operate continuously for extended periods, making them suitable for standby and prime power applications.
Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are generally more fuel-efficient than gasoline engines. They can provide a high amount of power output for a given amount of fuel.
High Power Density: Diesel generators have a high power density, meaning they can deliver a substantial amount of power in a relatively compact and lightweight package.
Long Operating Life: With proper maintenance, diesel generator sets can have a long operational life. Diesel engines are built to withstand heavy loads and continuous use.
Fuel Availability: Diesel fuel is widely available, making it easier to source fuel for generator sets. This is particularly advantageous in remote locations where other fuel types may be scarce.
Cold Weather Performance: Diesel engines generally perform well in cold weather conditions, making them suitable for use in regions with low temperatures.
Quick Start-up: Diesel generators can start and reach full operating capacity quickly, making them suitable for applications that require rapid response to power outages. Stable Power Output: Diesel generators provide a stable and consistent power output, with good voltage and frequency regulation.
Disadvantages
Environmental Impact: Diesel generators emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution. Strict emissions regulations may require additional emissions control systems.
Noise and Vibration: Diesel engines can be noisy and generate vibrations during operation. This may be a concern, especially in residential areas or applications requiring low noise levels.
Initial Cost: Diesel generator sets can have a higher upfront cost compared to some alternative power generation technologies.
Fuel Storage and Handling: Storing and handling diesel fuel may pose logistical challenges. Proper storage facilities and fuel quality maintenance are essential.
Maintenance Requirements: While diesel generators are durable, they still require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes tasks such as oil changes, filter replacements, and periodic inspections.
Emissions Compliance: Meeting increasingly stringent emissions regulations may require additional equipment or modifications, adding complexity and cost to the system.
Not Ideal for Small-Scale Applications: Diesel generators may not be the most cost-effective or efficient solution for very small-scale power needs, such as those of individual households.
What are the types of Diesel Generator Sets?
Diesel generator sets come in various types, each designed for specific applications and power requirements. The classification of diesel generator sets can be based on several factors, including their usage, size, and intended purpose. Here are some common types:
Standby Diesel Generators: These generators are designed to provide backup power in the event of a utility grid failure. They are commonly used in critical facilities such as hospitals, data centers, and emergency services.
Prime Power Diesel Generators: Prime power generators are intended to operate continuously for extended periods as the primary source of power. They are suitable for locations where there is no access to a reliable grid or as the main power source in off-grid applications.
Portable Diesel Generators: Portable generators are smaller, mobile units that are easy to transport. They are commonly used for construction sites, outdoor events, and as a temporary power source in various locations.
Industrial Diesel Generators: Industrial generators are designed for heavy-duty use in industrial applications. They often feature robust construction and are suitable for providing power to factories, manufacturing plants, and large industrial facilities.
Residential Diesel Generators: While less common than other types, there are diesel generators designed for residential use. These generators may be used in areas with unreliable grid power or in homes with specific power needs.
Marine Diesel Generators: Marine generators are designed for use on boats and ships. They are built to withstand the challenging conditions of marine environments and provide power for various onboard systems.
Trailer-Mounted Diesel Generators: These generators come mounted on trailers, making them easy to transport to different locations. They are often used in construction projects, events, and other temporary power needs.
Silent or Enclosed Diesel Generators: Silent generators are equipped with enclosures that help reduce noise levels during operation. They are suitable for applications where noise pollution needs to be minimized, such as in residential areas or events.
Hybrid Diesel Generators: Hybrid generators combine diesel power with other energy sources, such as solar or battery storage. This type of generator aims to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by incorporating alternative energy technologies.
Containerized Diesel Generators: Containerized generators are enclosed within shipping containers, providing a secure and weather-resistant housing. They are often used in applications where mobility, security, and protection from the elements are crucial.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a diesel generator set is a compact and reliable power generation system, combining a diesel engine and an electric generator. Widely utilized for backup and prime power needs, these sets offer durability, fuel efficiency, and rapid response during outages.